The discal hernication
A discal hernication is the bulging of a disk which happens in the spinal cord canal and causes a backward expulsion of the nucleus pulposus inside that canal.
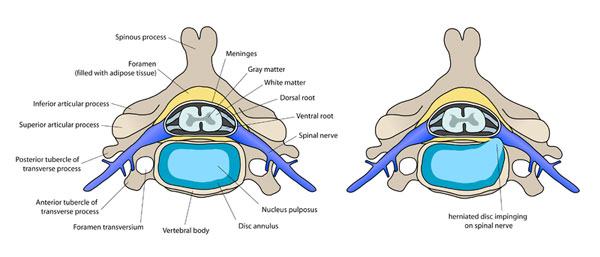
On the left side : a normal intervertebral disk. On the right side : a discal hernication.
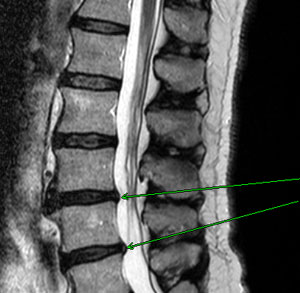 A discal hernication often happens in the last lumbar vertebras, because they are the ones that receive the most pressure when we are moving or when we have a trauma. Then, this can lead to a compression of the sciatic nerve roots. The hernication can occur in the cervical region (it then gives pain in the arm) or in the thoracic region (often asymptomatic). The more compressive is a discal hernication, the more it can lead to numbness in the affected area. For example, in an arm or in a leg.
A discal hernication often happens in the last lumbar vertebras, because they are the ones that receive the most pressure when we are moving or when we have a trauma. Then, this can lead to a compression of the sciatic nerve roots. The hernication can occur in the cervical region (it then gives pain in the arm) or in the thoracic region (often asymptomatic). The more compressive is a discal hernication, the more it can lead to numbness in the affected area. For example, in an arm or in a leg.
Risk factors
- Being overweight
- Chronic low back pain
- Pregnancy
- "Back pain" family history
- Intensive daily physical work
- Torsion movements
- Violent sports
- Stress
- 25 to 55 years old range
- Sedentarity
Medical interventions
Rest, plus anti-inflammatory, analgesics and muscle relaxants are often suggested by your physician. A surgical intervention can be conceivable in some cases only.
Physiotherapy treatments
Decrease the inflammation with :
- A device called ultrasound
- Ice
- Manual therapy and lumbar traction to decompress the affected nerve root
Regain the lost range of motion with :
- Soft articular mobilisations in the involved area
- Stretching exercises
Strengthen the muscles in order to reduce recidivism risks
- It will be way easier to execute the command given to your vertebral column when you have stronger muscles.
Find better working and training methods, more adapted to your condition.
Your physical therapist is the musculoskeletal disorders specialist. Don't wait before giving him a ring. He can help you recover your normal condition and get back to your activities that really mean something to you!